Meta Model Distinctions – Ill-Formed Statement – Distortions
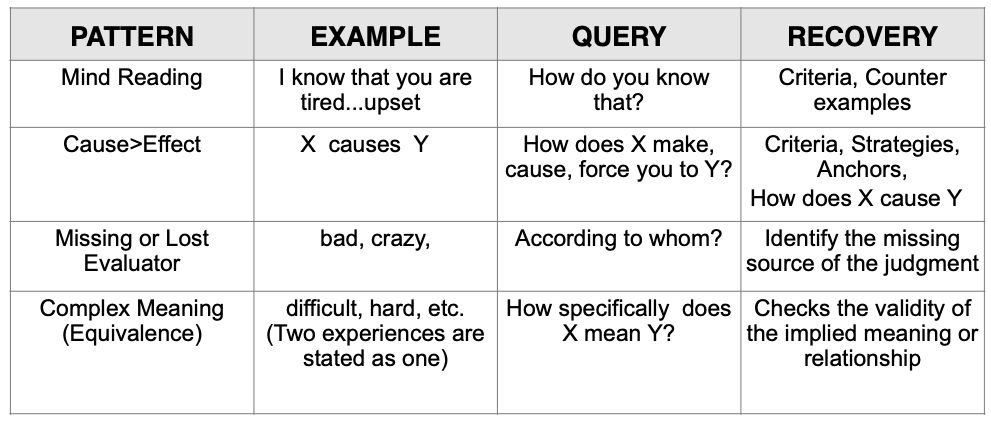
- Cause-Effect is a statement, which implies a causal link between a particular stimulus and a response. Listen for: ‘because’, ‘you/they make me’.
Examples of Cause-Effect are:
- “She made me so sad.”
- “His tone of voice makes me so angry.”
- “He caused me to yell at him.”
The Meta Model challenge to a Cause-Effect statement will identify the presupposed link (cause-effect) and can also recover complex equivalence and/or counter examples.
2. Mind Reading is a verbal pattern assuming knowledge of what another person thinks, feels, etc. It claims to know another’s internal experience.
Examples of Mind Reading are:
- “He doesn’t care about me.”
- “She did that on purpose.”
- “You don’t like me.”
The Meta Model challenge to Mind Reading identifies the criteria used to make assumptions about the other person’s internal state. It allows the speaker to question assumptions.
3. Missing or Lost Evaluators are verbal patterns of value judgments that leave out who performed the judgment and how it was made.
Examples of Lost Evaluators are:
- “It’s bad to be inconsistent.”
- “It’s selfish to think of your own feelings.”
- “That’s stupid.”
The Meta Model challenges to this pattern will recover the source of the value judgment, identify beliefs and generate awareness of other possibilities.
4. Complex Meaning (Equivalence) is a verbal pattern identifying when two experiences are interpreted as synonymous. It is a conclusion based on a belief that the outcome will always be the same.
Examples of Complex Meanings (Equivalence) are:
- “You’re yelling at me… you don’t care about me.”
- “He’s doing poorly in school… he has a learning problem.”
- “This material is too confusing… I’ll never learn it… I’m stupid.”
The Meta Model challenge to a Complex Meaning/Equivalence checks the validity of the relationship implied by the complex equivalence.
Distortions Recovery Chart